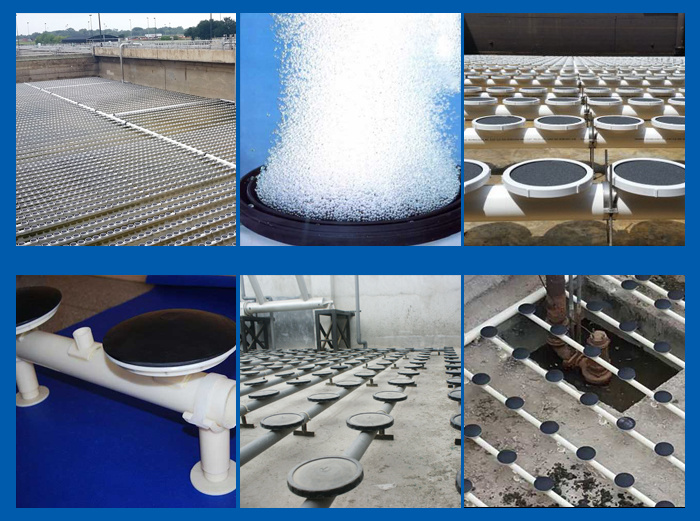
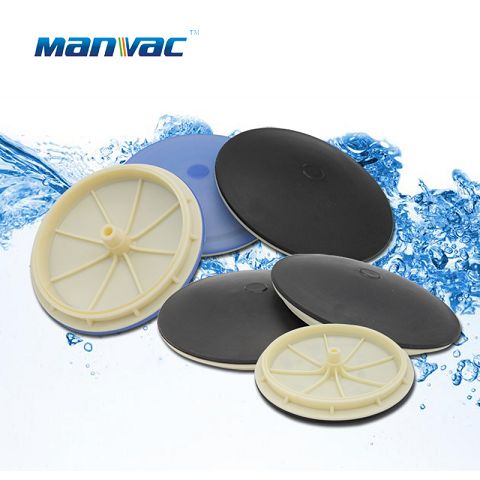
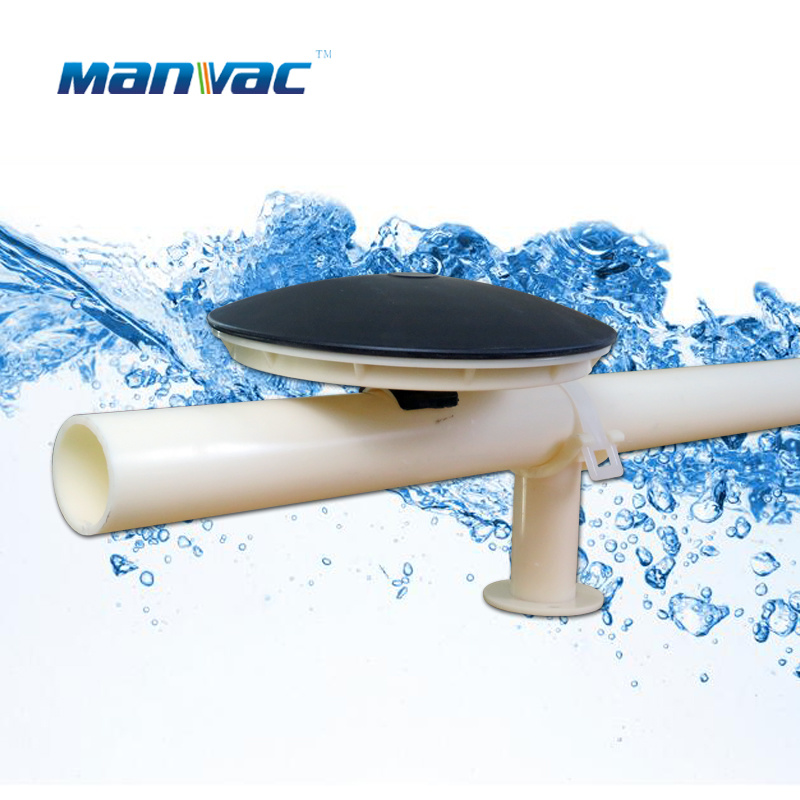
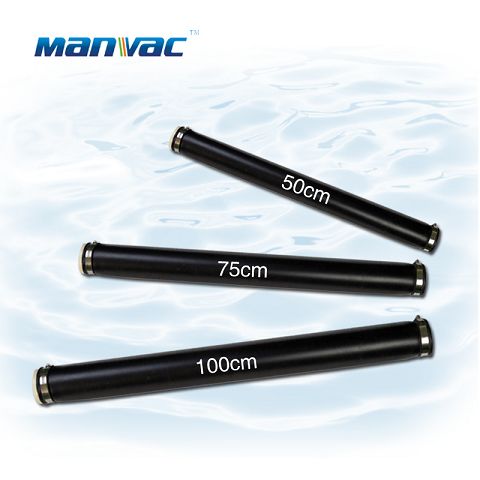
Home>Under Water Working Principle of Aerator
Products Categories
Contact Us
Tel: 15014788350
Fax: 0769-22800432
Mob: +86-15014788350
Email:
sales@manvac.cn
Add: Building C,Ming Zhi Shang Sha,Xi Ping,Nancheng,
Dongguan City, Guangdong Province,China 523000
 Spanish
Spanish English
English sales@manvac.cn
sales@manvac.cn +86-15014788350
+86-15014788350 Spanish
Spanish English
English